Selecting a workflow

Select workflow
- Placement workflow: User-submitted sequences are automatically added to a reference tree of the user's choice.
- De novo workflow: User is able to choose from which additional species to construct the tree in detail, and can choose which genes to use for the MLST.
Placement workflow
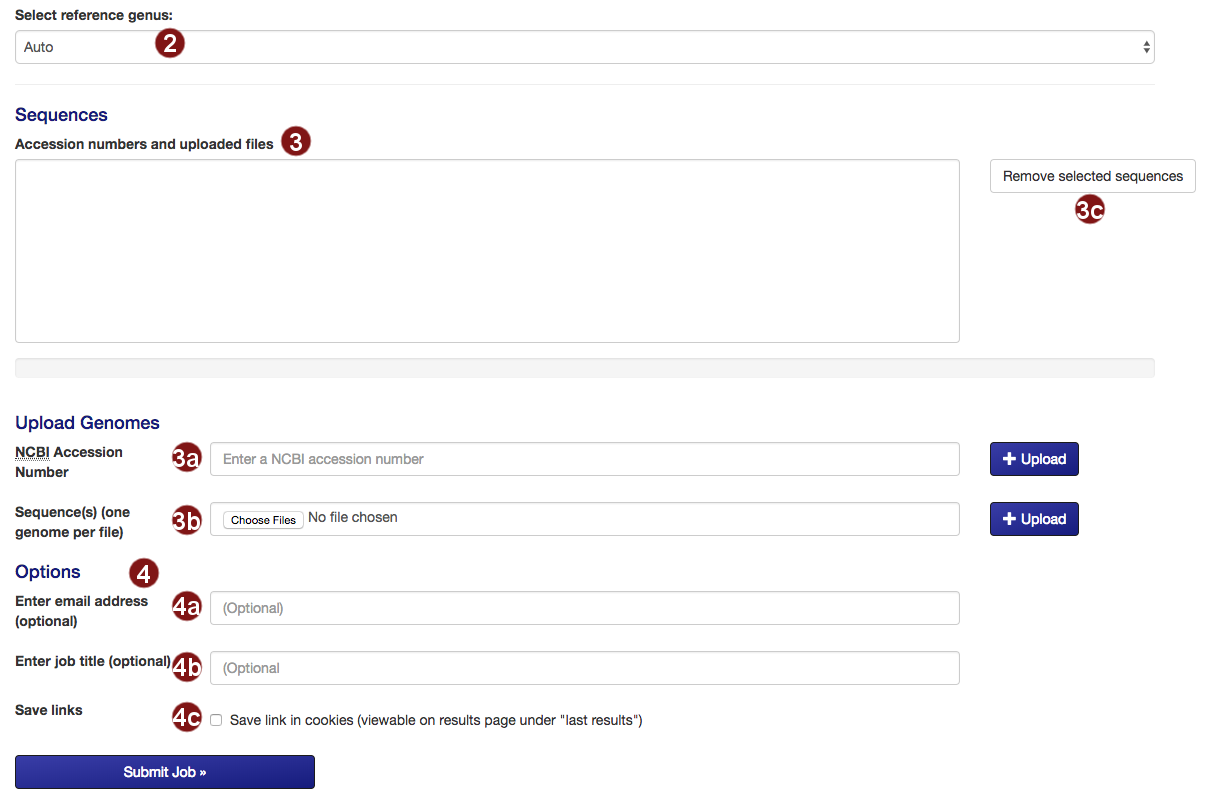
- Select the reference tree to which the uploaded sequences will be added. By default, autoMLST will attempt to detect the closest genus on its own.
- Submit the sequences to be added to the tree.
- Retrieve an NCBI sequence by its accession number.
- Upload one or multiple sequence files. Acceptable formats are FASTA, Genbank (and EMBL?) files.
Please make sure that each file only contains the genome of one organism. - Remove selected sequences from the list.
Note: a maximum of 50 sequences may be added to the tree. - Several additional options for saving job results and being notified about job status are available:
- Optional: submit an email address so you can be notified about the status of your autoMLST job.
- Optional: give your job a descriptive title.
Note: you will not be able to search for your job by its title, only by its job ID. - Optional: save a link to the job in a list of your recent jobs on the Results
page.
Note: saving links of your recent jobs requires setting a cookie. For information on our use of cookies see below.
Denovo workflow
Step 1 Sequence submission
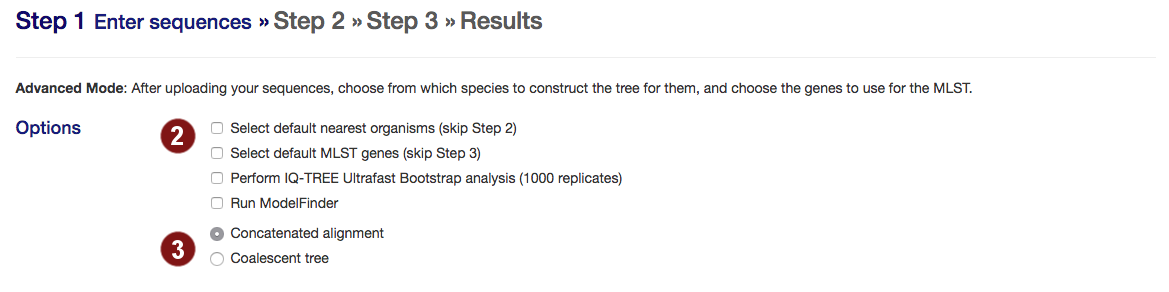
- Select options:
- skip manual selection of organisms for tree construction (step 2) or genes to align (step 3) and automatically proceed with the best 50 organisms or best 100 genes when they are found.
- perform bootstrapping with Ultrafast Bootstrap (default: no bootstrapping)
- run ModelFinder to find the optimal model for tree building
- autoMLST can create either a concatenated alignment or a coalescent tree.
- Concatenated alignment: the standard MLSA. This strategy performs better if most gene trees don't diverge from the species tree or diverge very little.
- Coalescent tree: constructs the species tree from the individual gene trees. This strategy performs better than concatenated alignments if there are large differences between a gene tree and the species tree. However, if phylogenetic signal is only present in some sequences, it may be lost.
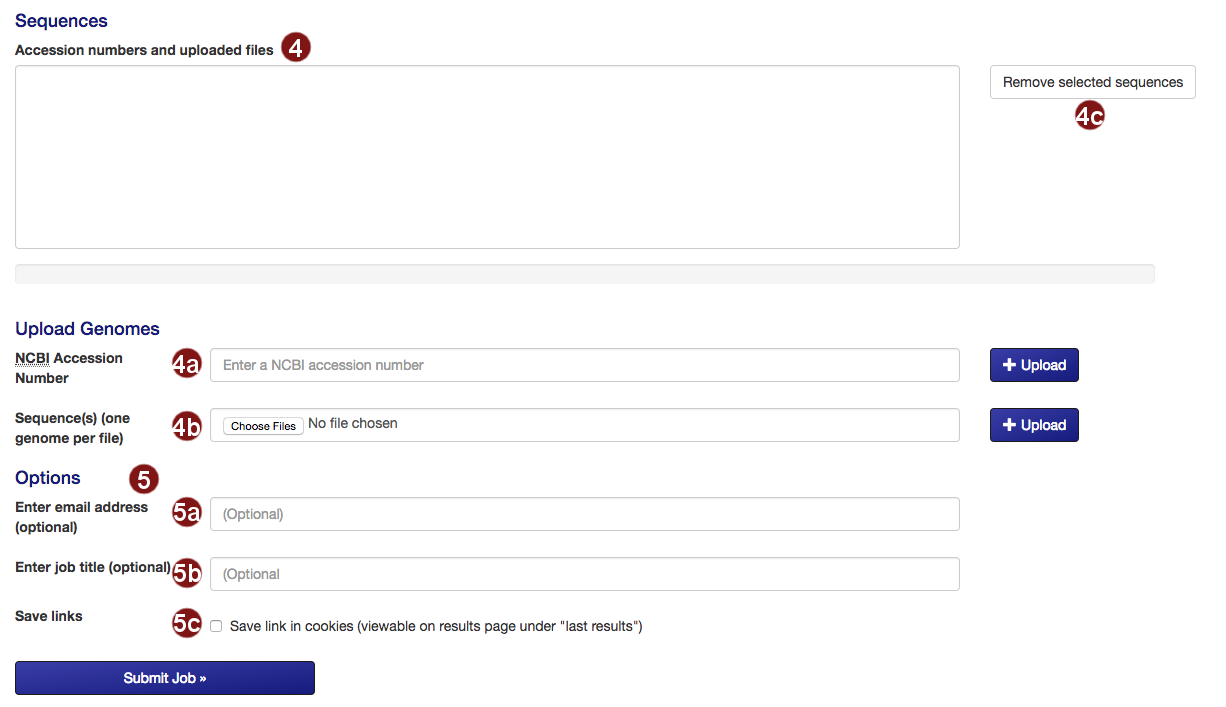
- Submit the sequences to construct the tree.
- Retrieve an NCBI sequence by its accession number.
- Upload one or multiple sequence files. Acceptable formats are FASTA, Genbank (and EMBL?) files.
Please make sure that each file only contains the genome of one organism. - Remove selected sequences from the list.
Note: a maximum of 50 sequences may be added to the tree. - Several additional options for saving job results and being notified about job status are available:
- Optional: submit an email address so you can be notified about the status of your autoMLST job.
- Optional: give your job a descriptive title.
Note: you will not be able to search for your job by its title, only by its job ID. - Optional: save a link to the job in a list of your recent jobs on the Results
page.
Note: saving links of your recent jobs requires setting a cookie. For information on our use of cookies see below.
Step 2 Species and outgroup selection
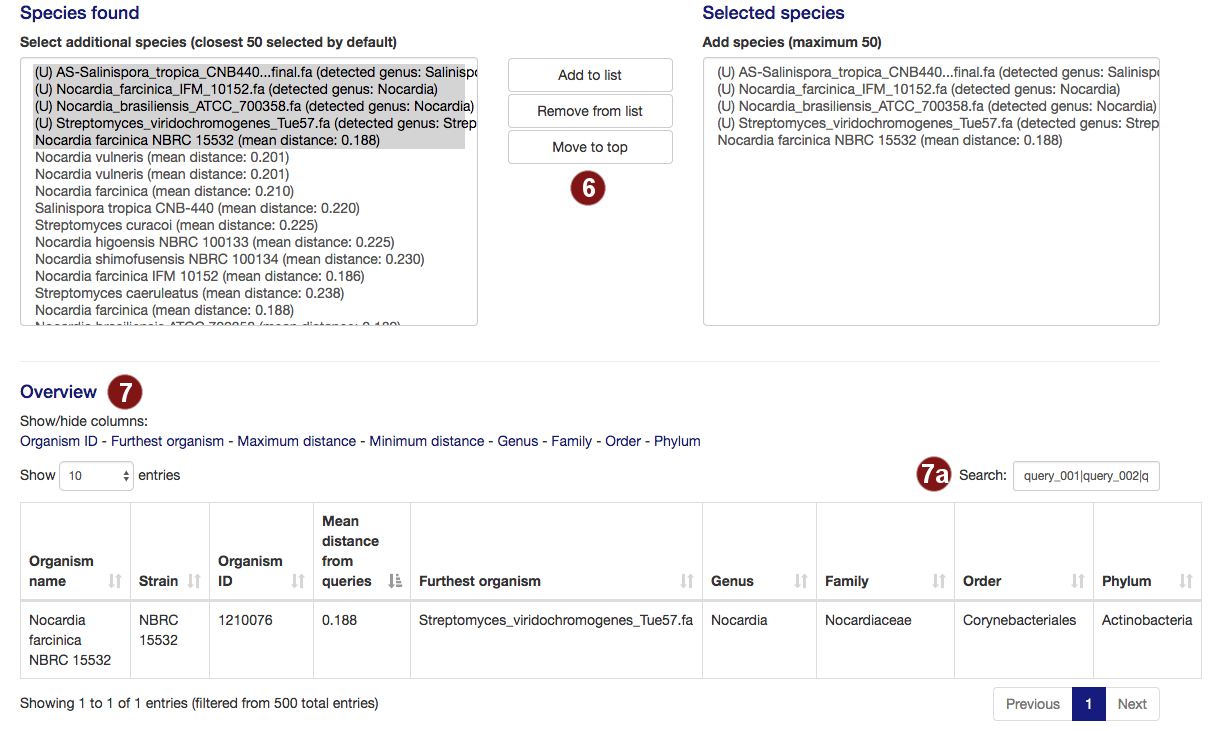
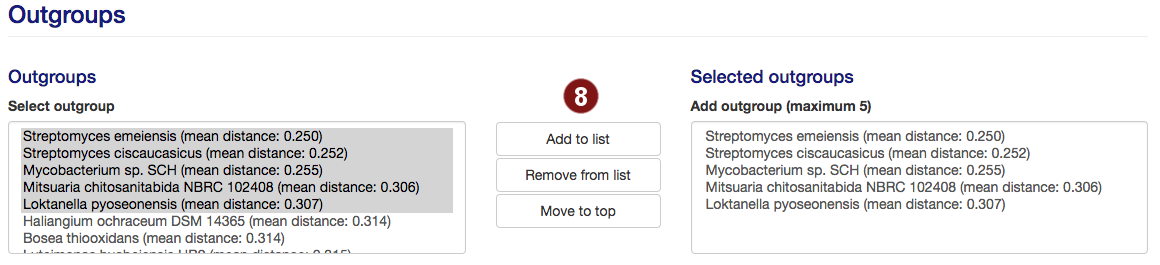
- By default, autoMLST picks all user-submitted sequences and the closest organisms it detects to
continue, to a total of 50. Users are able to add organisms from the organism list to this selection
or remove them.
Note: A maximum of 50 organisms will be used for tree construction; additional species above this number will not be used. Sequences past this limit are highlighted in red. - Additional information on the selected species is displayed, sorted by the mean distance to the
query sequences by default. Users can pick what information is displayed by choosing options to
show/hide columns.
- By default, the table is filtered to only display information on the sequences the user selected. However, users may search the table for species, genera, families, orders or phyla by their name or the taxonomy ID numbers assigned by the NCBI.
- By default, up to 5 species are used for outgroups. Users are able to add organisms from the
outgroup list to this selection or remove them.
Note: A maximum of 5 outgroups will be used; additional species above this number will not be used. Sequences past this limit are highlighted in red.
Step 3 Gene selection
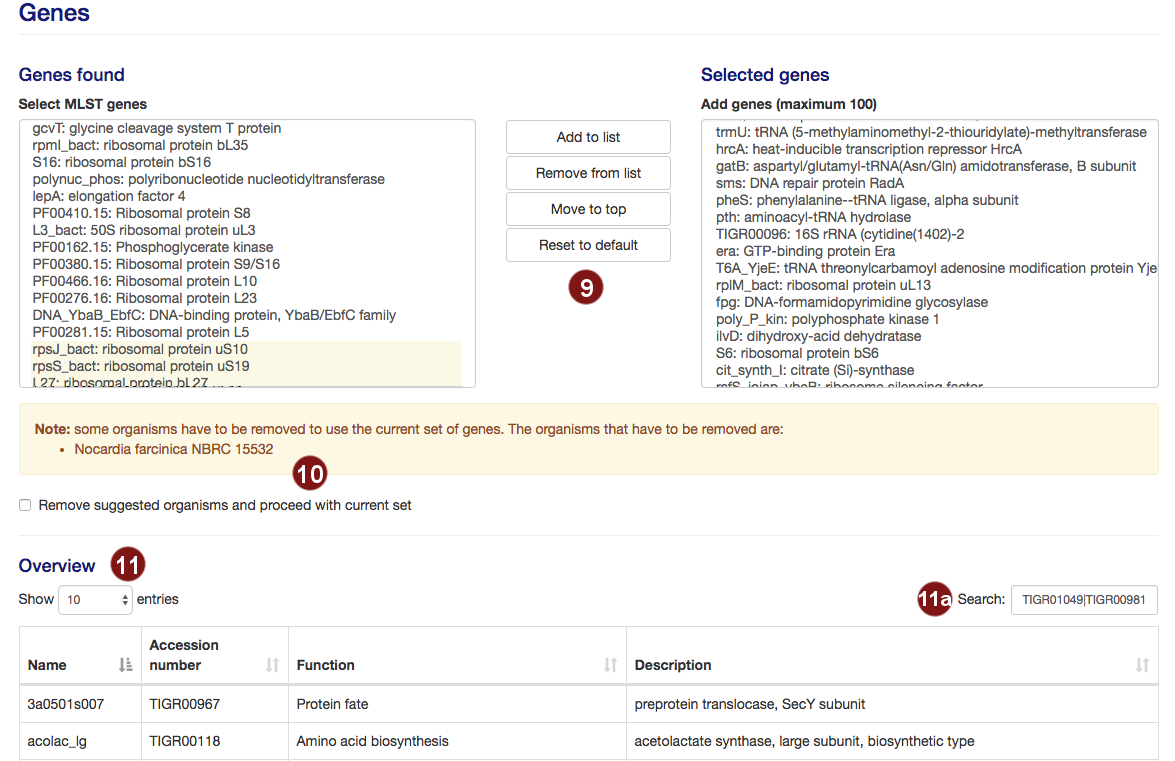
- autoMLST selects 100 genes for the MLST by default. Users are able to add or remove genes from this
selection.
Note: A maximum of 100 genes will be used for the MLST; additional genes above this number will not be used. - Not all potential MLST genes may be found in all selected species. In this case, a warning will be
displayed and the species limiting the number of MLST genes listed.
Users then have the choice to remove the listed organisms in order to proceed with their selection.
Genes which require the deletion of one or more organisms are highlighted in yellow. - Additional information on the selected genes is displayed, sorted by gene name by default.
- By default, the table is filtered to only display information on the sequences the user selected. However, users may search the table for genes by their name, accession number, function or description.
Results
Mash-based ANI estimation
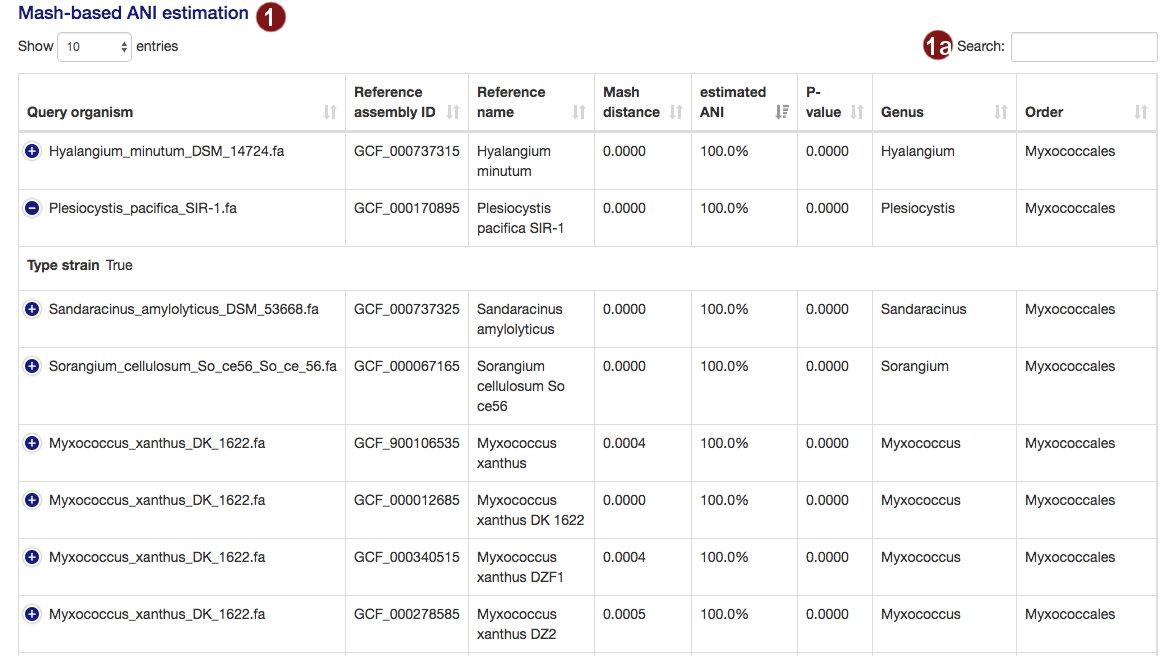
- Both during the loading screens and in the final results page, the user is presented with a table of the
organisms closest to their submitted sequences, as determined by an estimate of the average nucleotide
identity. The table is sorted by highest ANI by default. The
amount of information displayed in the table by default depends on screen width; users may view the remaining
information by clicking the row in question.
- Users may search the table for organisms by their name, genus, order or the ID of a reference genome assembly.
Tree
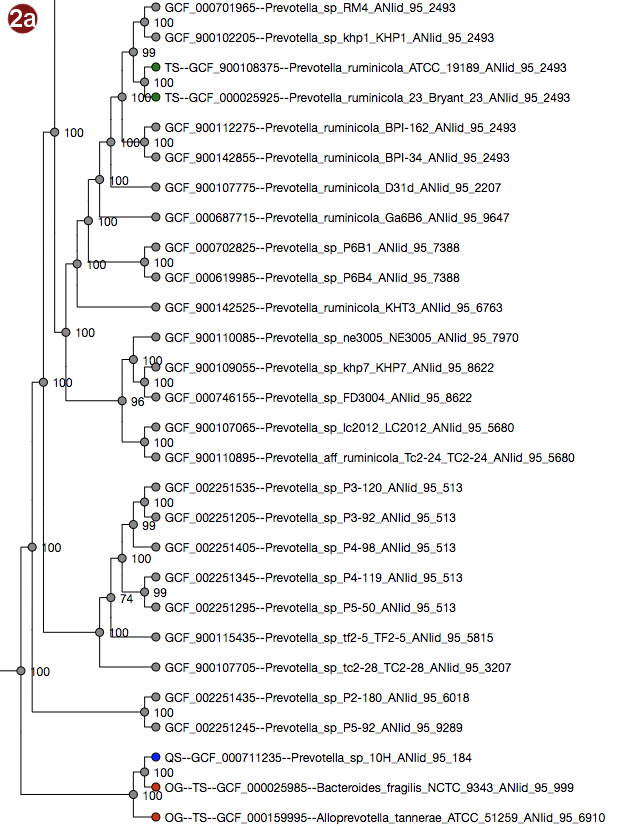

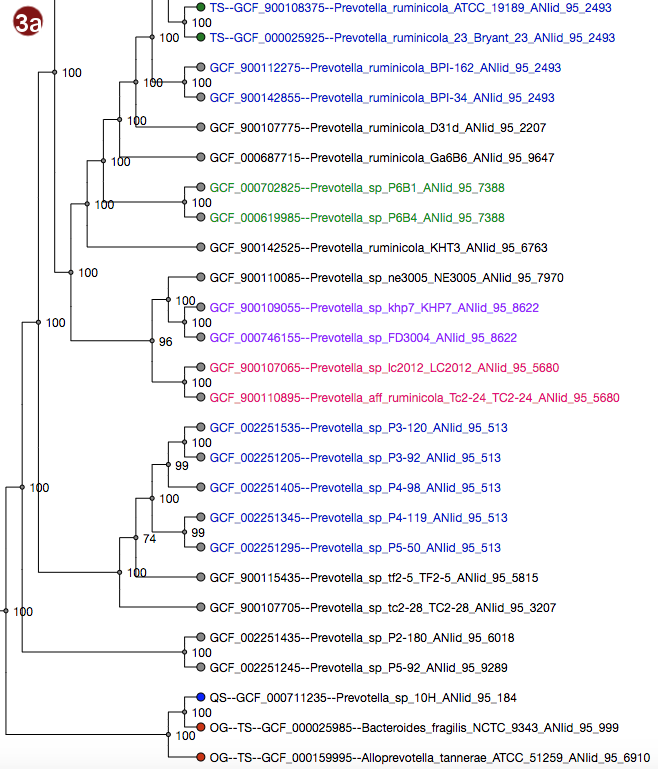
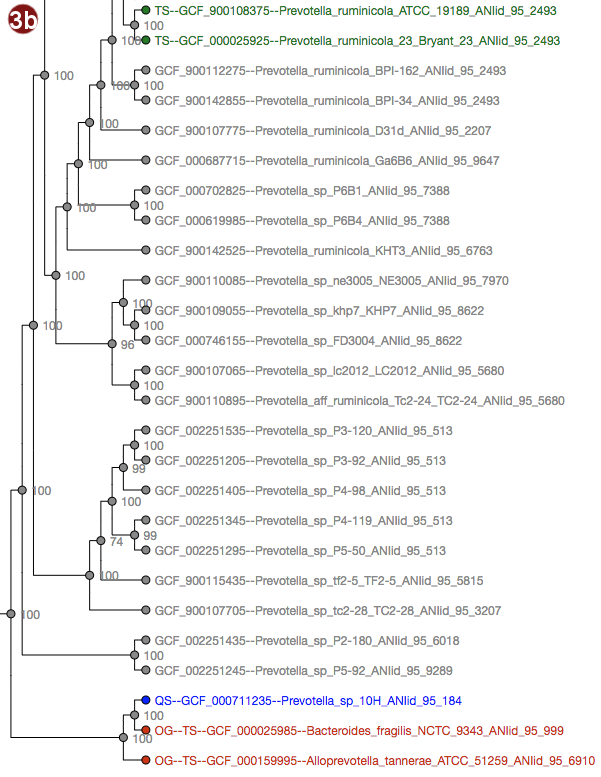
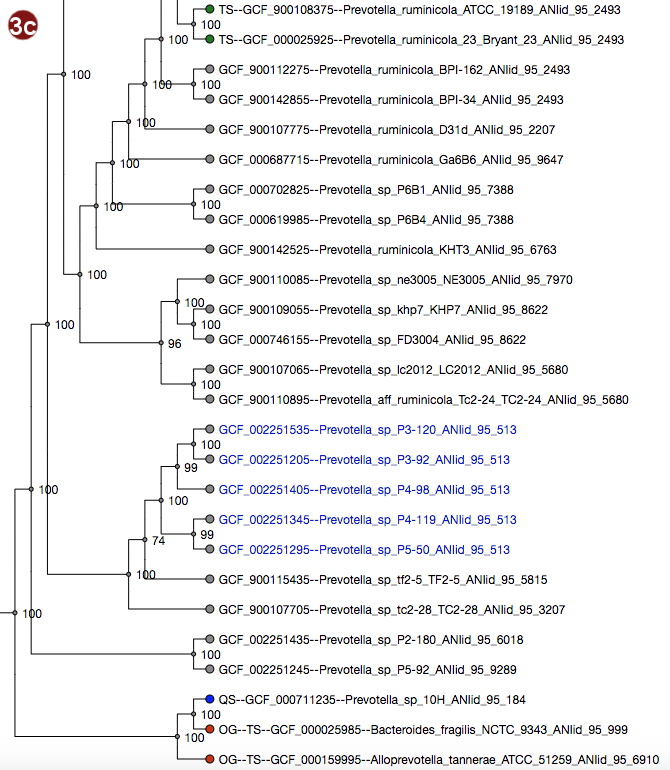

Depending on selected workflow and user choices, a tree generated from a multilocus sequence alignment, a
coalescent tree or a tree generated by addition of user sequences to a reference tree is presented to the
user.
User-submitted sequences are prefixed with the abbreviation "QS"; their respective nodes are colored blue.
Outgroups are prefixed with the abbreviation "OG";their respective nodes are colored red.
Type strains are prefixed with the abbreviation "TS"; their respective nodes are colored green.
It is also possible to search for organisms in the tree; organisms matching the search term are displayed with
a larger font size.
Several details about tree visualization may be changed by the user:
- The tree can be resized horizontally in steps of 100 pixels.
- The tree may be displayed in two different ways: with unscaled branch lengths, as a rectangular cladogram (2a), or with scaled branch lengths, as a rectangular phylogram (2b).
- Label coloration may be changed in several ways:
- All organisms in the reference database have been grouped by their pairwise ANI as approximated by Mash; see the About page for details; all of these groupings may be visualized by label color under the option "Display ANI groups" (note that label colors may be repeated). ANI groups were identified using levels from 95%-99% sequence similarity as cutoff; all these different groups may be displayed.
- Type strain, outgroup and query sequence coloration may also be applied to the labels by selecting "Display strain info". Organisms that are neither a type strain, an outgroup nor a query sequence are grayed out in this display.
- By clicking an organism's label, it is also possible to highlight only the ANI group containing this organism in the tree. The last selected cutoff level for the whole tree is used; if no cutoff level has been selected, the cutoff used is 95%. Note that this has no effect for organisms that do not belong to any group at this cutoff.
Note that the example images show Ultrafast Bootstrap values. Depending on user choices and workflow, the tree may display likelihood values (in the default workflow), Ultrafast Bootstrap values or no support values at all (in the advanced workflow). For interpretation of the support values, please refer to the About page.
Additional information is also available:
- Users may download
- the tree in Newick format (without colors)
- an image of the tree in .svg format (with colors)
- a compressed folder of the alignments from which it was constructed
- the list of genes used in the MLSA
- the list of organisms used
- the full list of estimated ANIs between their organisms and the reference organisms.
In the advanced workflow, it is also possible to redo the analysis with different additional species and MLST genes by selecting "reanalyze from Step 2". Note that this will clear the existing results for this job.
Cookies
Users may choose to store the link to a job they submit in their last results (accessible on the results page). This is done via cookies; selecting the option to store the link means you consent to autoMLST's use of cookies for this. Cookies are only stored for the purpose of remembering the job numbers of the jobs submitted by the user; all that is stored is the job number.